079762
Simple steps to safety self audit tool results
 line
line
 line
line
 line
line
 line
line
 line
line
 line
line
 line
line
You’re on the right track, but there is more you can do to help with defining safety roles and responsibilities.
Your responses indicate that you need to be more consistent with your approach to health and safety. Ask yourself: Are safety responsibilities effectively communicated? Have you allowed adequate resources to meet safety responsibilities? Are you involved in safety issues?
What you can do to improve:
Ensure safety responsibilities are clearly defined and understood
Your workers will contribute to safety if they understand their responsibilities; and have the skills to meet those responsibilities.
Are your workers given induction training that includes safety information and outlines their safety responsibilities? Do they have clear instructions on how to deal with safety issues? Do supervisors understand their role in ensuring safety in the workplace?
Review resources to support safety initiatives
Demonstrate your commitment by providing enough time and money to deal with safety problems and to fix problems when they arise. Where problems cannot be fixed immediately, provide an alternate solution.
Demonstrate your commitment
Get actively involved with safety issues when they arise. Attend workplace meetings regularly. Speak with your workers and act upon their feedback. Ensure solutions to safety problems are implemented promptly by those responsible.
Useful links
You’re on the right track, but there is more you can do to help with defining safety roles and responsibilities.
Your responses indicate that you need to be more consistent with your approach to health and safety. Ask yourself: Are safety responsibilities effectively communicated? Have you allowed adequate resources to meet safety responsibilities? Are you involved in safety issues?
What you can do to improve:
Ensure safety responsibilities are clearly defined and understood
Your workers will contribute to safety if they understand their responsibilities; and have the skills to meet those responsibilities.
Are your workers given induction training that includes safety information and outlines their safety responsibilities? Do they have clear instructions on how to deal with safety issues? Do supervisors understand their role in ensuring safety in the workplace?
Review resources to support safety initiatives
Demonstrate your commitment by providing enough time and money to deal with safety problems and to fix problems when they arise. Where problems cannot be fixed immediately, provide an alternate solution.
Demonstrate your commitment
Get actively involved with safety issues when they arise. Attend workplace meetings regularly. Speak with your workers and act upon their feedback. Ensure solutions to safety problems are implemented promptly by those responsible.
Useful links
There are consultation procedures in place but these may not be working effectively or capturing all of your workers’ input.
Your responses indicate that you do consult with your workers but that it is inconsistent or that you may not reach all of your workers. You may also not provide feedback or consult with all relevant workers about health and safety matters.
What you can do to improve:
Make sure that your consultation process is suitable for the workplace
Your consultation process may need to be changed to take into account the different needs of your workers, the size of your business, the location of your site or sites if you have more than one, shift arrangements, transport workers or workers who work at client sites or any other special arrangements you may have with your workers. Some workers may not be able to attend regular meetings and may be missing vital information about their safety or changes in the workplace. You may need to introduce alternative methods of consulting with these workers.
Encourage workers to consult and always provide feedback
Sometimes workers can appear to lack the desire to consult but that may be as a result of the process of consultation rather than the consultation itself.
You can help address this by:
- Scheduling safety meetings as a priority. If safety meetings are held at the end of the day or a shift, you can run out of time and workers may feel rushed or too tired to contribute. Schedule safety meetings at the start of the day or shift so that there is enough time and workers are fresh and alert.
- Show that you value your workers’ views. You can develop a method to demonstrate to your workers that their concerns and feedback are considered. This could be in the form of an action plan or some other method that clearly shows you are listening. Sometimes workers are told about decisions rather than being consulted. If your workers believe their concerns are ignored they will be reluctant to participate in the consultation process. Don’t make safety decisions without regard to your workers’ feedback. If a decision is made that is contrary to worker views, provide reasons that clearly outline why.
- Involve your entire workforce. Some of your workers may be unaware of their WHS responsibilities. Train all of your workers in WHS consultation procedures, including your supervisors and managers. Workers from non-English speaking backgrounds and those with special needs should be consulted individually to ensure their concerns are addressed.
- To be effective, consultation needs to be consistent and inclusive and safety issues need to be addressed in a timely way. Discuss safety concerns as part of your regular workplace meetings rather than ad-hoc meetings. Making safety part of the regular agenda and having meaningful discussion will go a long way to integrating safety into the normal business culture and demonstrating to your workers that it is an important aspect of business operations.
Useful links
There are consultation procedures in place but these may not be working effectively or capturing all of your workers’ input.
Your responses indicate that you do consult with your workers but that it is inconsistent or that you may not reach all of your workers. You may also not provide feedback or consult with all relevant workers about health and safety matters.
What you can do to improve:
Make sure that your consultation process is suitable for the workplace
Your consultation process may need to be changed to take into account the different needs of your workers, the size of your business, the location of your site or sites if you have more than one, shift arrangements, transport workers or workers who work at client sites or any other special arrangements you may have with your workers. Some workers may not be able to attend regular meetings and may be missing vital information about their safety or changes in the workplace. You may need to introduce alternative methods of consulting with these workers.
Encourage workers to consult and always provide feedback
Sometimes workers can appear to lack the desire to consult but that may be as a result of the process of consultation rather than the consultation itself.
You can help address this by:
- Scheduling safety meetings as a priority. If safety meetings are held at the end of the day or a shift, you can run out of time and workers may feel rushed or too tired to contribute. Schedule safety meetings at the start of the day or shift so that there is enough time and workers are fresh and alert.
- Show that you value your workers’ views. You can develop a method to demonstrate to your workers that their concerns and feedback are considered. This could be in the form of an action plan or some other method that clearly shows you are listening. Sometimes workers are told about decisions rather than being consulted. If your workers believe their concerns are ignored they will be reluctant to participate in the consultation process. Don’t make safety decisions without regard to your workers’ feedback. If a decision is made that is contrary to worker views, provide reasons that clearly outline why.
- Involve your entire workforce. Some of your workers may be unaware of their WHS responsibilities. Train all of your workers in WHS consultation procedures, including your supervisors and managers. Workers from non-English speaking backgrounds and those with special needs should be consulted individually to ensure their concerns are addressed.
- To be effective, consultation needs to be consistent and inclusive and safety issues need to be addressed in a timely way. Discuss safety concerns as part of your regular workplace meetings rather than ad-hoc meetings. Making safety part of the regular agenda and having meaningful discussion will go a long way to integrating safety into the normal business culture and demonstrating to your workers that it is an important aspect of business operations.
Useful links
You identify and control some or most of your hazards and risks but you may not have effective safe work procedures in place for all of them.
Your responses indicate that you have started to address the risks associated with work tasks but you may need to look more closely at the tasks, identify any hazards you may have overlooked, and ensure that your safe work procedures are appropriate and help your workers do their jobs safely.
What you can do to improve:
Review work tasks
Inspect the workplace and review all tasks. Check for risks including:
- using chemicals
- lifting and moving products
- working at heights
- slips, trips and falls
- electrical equipment
- housekeeping.
Make sure you talk with your workers and involve them in identifying hazards associated with their work. Develop and implement safe work procedures for those tasks that pose a risk.
Plan your approach
Sometimes, business pressures or uncertainty about what to do next may delay the development and implementation of safe work procedures.
Plan the process carefully so that you are able to develop safe work procedures gradually, within the constraints of your business demands. You should prioritise those tasks with the highest risk and involving the entire workforce in a structured way will help a lot with time. A good plan will help you overcome the limitations in time and resources and will let you track progress against targets.
Ensure procedures are up-to-date
If you find that your workers are not always following safe work procedures, review the procedures to ensure they are still relevant and are up to date. Sometimes procedures are not followed because they use old methods or talk about steps or machines that are no longer in use. If procedures are up to date, have your workers been trained in their use? Are your workers being properly supervised? Do your supervisors and managers make sure they always follow the procedures?
Useful links
You identify and control some or most of your hazards and risks but you may not have effective safe work procedures in place for all of them.
Your responses indicate that you have started to address the risks associated with work tasks but you may need to look more closely at the tasks, identify any hazards you may have overlooked, and ensure that your safe work procedures are appropriate and help your workers do their jobs safely.
What you can do to improve:
Review work tasks
Inspect the workplace and review all tasks. Check for risks including:
- using chemicals
- lifting and moving products
- working at heights
- slips, trips and falls
- electrical equipment
- housekeeping.
Make sure you talk with your workers and involve them in identifying hazards associated with their work. Develop and implement safe work procedures for those tasks that pose a risk.
Plan your approach
Sometimes, business pressures or uncertainty about what to do next may delay the development and implementation of safe work procedures.
Plan the process carefully so that you are able to develop safe work procedures gradually, within the constraints of your business demands. You should prioritise those tasks with the highest risk and involving the entire workforce in a structured way will help a lot with time. A good plan will help you overcome the limitations in time and resources and will let you track progress against targets.
Ensure procedures are up-to-date
If you find that your workers are not always following safe work procedures, review the procedures to ensure they are still relevant and are up to date. Sometimes procedures are not followed because they use old methods or talk about steps or machines that are no longer in use. If procedures are up to date, have your workers been trained in their use? Are your workers being properly supervised? Do your supervisors and managers make sure they always follow the procedures?
Useful links
Your organisation has started to address health and wellbeing and views it as important, however, there are no formal plans or programs in place.
Workers are encouraged to report psychological hazards/risks but it is likely that there is no formal mechanism to do this so it tends to be word of mouth. Whilst there is some education around the prevention of bullying and harassment, this can be improved by formalising procedures and ensuring all workers are aware of how to report unreasonable behaviour.
What you can do to improve:
Plan your approach
There is increased awareness of the importance of health and wellbeing in workplaces, however, sometimes workplaces are unclear on how it can be addressed in a planned and proactive manner. This can be achieved by developing a formal health and wellbeing action plan/program. Important steps include getting management on board, reviewing what you have and don’t have in place, asking staff what they think is important to their health and wellbeing and then developing a plan/program of health and wellbeing activities based on this information. It is important to communicate this plan to workers so they know what activities they can be involved in. In this way, health promotion activities such as mental health, healthy eating, physical activity, drug and alcohol, etc. are regular events during the year, and address the needs of the workforce.
If you are looking for further tools and resources in this area, go to the Heads Up Website and SA Health “How to create a healthy workplace “resources and toolkit.
Ensure your health and safety system includes managing psychological hazards and risks
The employer has a legal obligation to eliminate or minimise risks to the health and safety of workers (as is reasonably practicable). Under the WHS laws, the definition of “health” includes both physical and psychological health. Therefore, it is important that workers are encouraged to report hazards that can contribute to work-related stress, such as high workloads, exposure to traumatic events, work-related violence, fatigue and poor workplace relationships. This should be integrated into standard incident reporting procedures so workers know how to report these types of issues, the incidents can be appropriately investigated and suitable control measures can be put in place.
One psychological hazard which is important to address and prevent in workplaces is bullying and harassment. Whilst your workplace may conduct some education on what is acceptable and unacceptable workplace behaviour, it is important that your workplace’s bullying and harassment policy and procedures and any code of conduct is part of induction procedures, and is reinforced through refresher training. Workplace bullying behaviours should not be tolerated and early reporting of these behaviours should be encouraged. Workers should have a clear understanding of what is bullying and harassment and how to report unreasonable behaviour. The workplace’s procedures should also include how reports of bullying will be appropriately investigated and responded to. If a worker considers they are being bullied, they will be more likely to report it if they know there is a transparent reporting process in place and that it will be followed as soon as a report is received.
For more information on managing work-related psychological health and safety, go to a Safe Work Australia “Work-related psychological health and safety. A systematic approach to meeting your duties”.
For more information on the prevention of bullying, go to Safe Work Australia “Guide for Preventing and Responding to Workplace Bullying”.
Your organisation has started to address health and wellbeing and views it as important, however, there are no formal plans or programs in place.
Workers are encouraged to report psychological hazards/risks but it is likely that there is no formal mechanism to do this so it tends to be word of mouth. Whilst there is some education around the prevention of bullying and harassment, this can be improved by formalising procedures and ensuring all workers are aware of how to report unreasonable behaviour.
What you can do to improve:
Plan your approach
There is increased awareness of the importance of health and wellbeing in workplaces, however, sometimes workplaces are unclear on how it can be addressed in a planned and proactive manner. This can be achieved by developing a formal health and wellbeing action plan/program. Important steps include getting management on board, reviewing what you have and don’t have in place, asking staff what they think is important to their health and wellbeing and then developing a plan/program of health and wellbeing activities based on this information. It is important to communicate this plan to workers so they know what activities they can be involved in. In this way, health promotion activities such as mental health, healthy eating, physical activity, drug and alcohol, etc. are regular events during the year, and address the needs of the workforce.
If you are looking for further tools and resources in this area, go to the Heads Up Website and SA Health “How to create a healthy workplace “resources and toolkit.
Ensure your health and safety system includes managing psychological hazards and risks
The employer has a legal obligation to eliminate or minimise risks to the health and safety of workers (as is reasonably practicable). Under the WHS laws, the definition of “health” includes both physical and psychological health. Therefore, it is important that workers are encouraged to report hazards that can contribute to work-related stress, such as high workloads, exposure to traumatic events, work-related violence, fatigue and poor workplace relationships. This should be integrated into standard incident reporting procedures so workers know how to report these types of issues, the incidents can be appropriately investigated and suitable control measures can be put in place.
One psychological hazard which is important to address and prevent in workplaces is bullying and harassment. Whilst your workplace may conduct some education on what is acceptable and unacceptable workplace behaviour, it is important that your workplace’s bullying and harassment policy and procedures and any code of conduct is part of induction procedures, and is reinforced through refresher training. Workplace bullying behaviours should not be tolerated and early reporting of these behaviours should be encouraged. Workers should have a clear understanding of what is bullying and harassment and how to report unreasonable behaviour. The workplace’s procedures should also include how reports of bullying will be appropriately investigated and responded to. If a worker considers they are being bullied, they will be more likely to report it if they know there is a transparent reporting process in place and that it will be followed as soon as a report is received.
For more information on managing work-related psychological health and safety, go to a Safe Work Australia “Work-related psychological health and safety. A systematic approach to meeting your duties”.
For more information on the prevention of bullying, go to Safe Work Australia “Guide for Preventing and Responding to Workplace Bullying”.
Your workers are unlikely to be properly trained or supervised whilst at work.
Your responses indicate that you need to take immediate action to provide training to your workers in their roles and in safe work practices generally. You may also need to review your supervisory arrangements to ensure workers are receiving adequate and consistent supervision.
What you can do to improve:
Establish a safety induction process
When you employ a new worker, train them in your policies, procedures and the expected behaviours. Induction training should include:
- health and safety roles and responsibilities
- how and when to report safety issues and incidents
- your consultation process
- general safety rules such as the use of personal protective equipment
- emergency procedures
- training in specific tasks.
Make sure you review your induction and training information periodically to ensure it is up-to-date and relevant. You can provide the training in a manual for your workers to reference but the manual is for reference only – it is not a substitute for you personally training your workers.
Provide adequate supervision
What is considered relevant supervision will be largely dependent on the role, associated hazards and risks, the experience of the worker, any language or understanding barriers or any other factor that may be pertinent in the worker’s circumstances.
Supervision of workers is a good way for you to be sure that your workers are working safely and following your procedures.
Practice what you preach
If your workers see you or your supervisors flaunting the procedures, taking shortcuts or otherwise failing to follow the established safe work practices they will likely do the same. This leads to dangerous work practices which will in turn inevitably cause injury.
Useful links
Your workers are unlikely to be properly trained or supervised whilst at work.
Your responses indicate that you need to take immediate action to provide training to your workers in their roles and in safe work practices generally. You may also need to review your supervisory arrangements to ensure workers are receiving adequate and consistent supervision.
What you can do to improve:
Establish a safety induction process
When you employ a new worker, train them in your policies, procedures and the expected behaviours. Induction training should include:
- health and safety roles and responsibilities
- how and when to report safety issues and incidents
- your consultation process
- general safety rules such as the use of personal protective equipment
- emergency procedures
- training in specific tasks.
Make sure you review your induction and training information periodically to ensure it is up-to-date and relevant. You can provide the training in a manual for your workers to reference but the manual is for reference only – it is not a substitute for you personally training your workers.
Provide adequate supervision
What is considered relevant supervision will be largely dependent on the role, associated hazards and risks, the experience of the worker, any language or understanding barriers or any other factor that may be pertinent in the worker’s circumstances.
Supervision of workers is a good way for you to be sure that your workers are working safely and following your procedures.
Practice what you preach
If your workers see you or your supervisors flaunting the procedures, taking shortcuts or otherwise failing to follow the established safe work practices they will likely do the same. This leads to dangerous work practices which will in turn inevitably cause injury.
Useful links
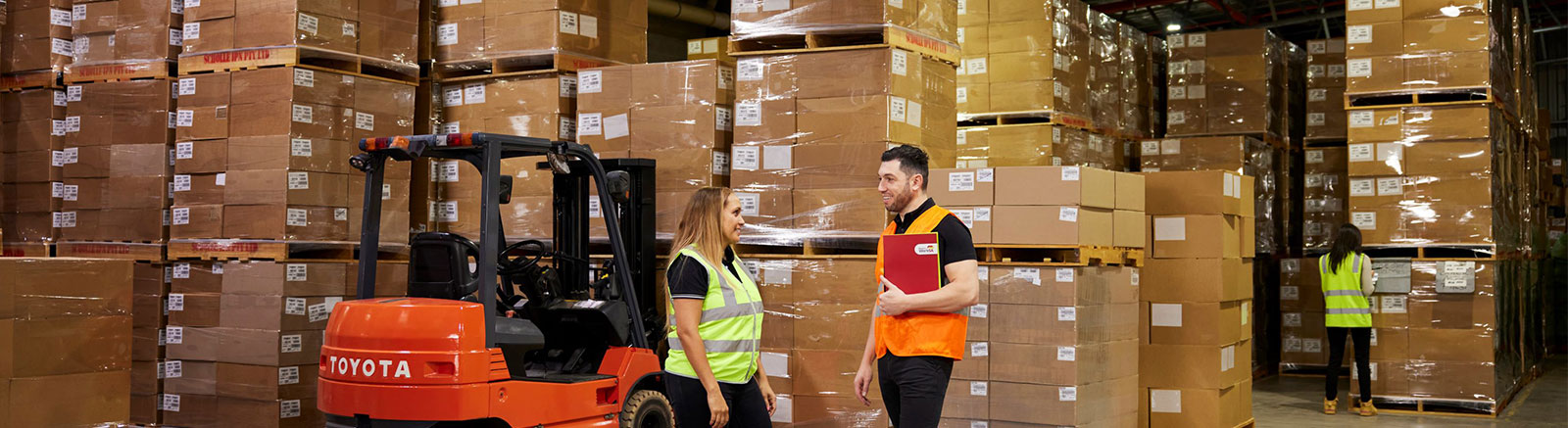
You are unlikely to have any processes in place for ensuring that your workplace is safe.
This score indicates that you need to take immediate action to ensure you maintain a safe workplace.
What you can do to improve:
Design and implement a process to carry out regular safety checks
You need to set up a system of regular safety inspections of your worksite. These inspections should be scheduled and there should be checks performed to make sure they occur as planned. Once you have established a routine, it is a good idea to have a regular rotation of people doing the inspection including managers, supervisors and workers.
Any issues you note as part of these inspections should be documented and actioned. Always inform workers that this has occurred as it will help keep them involved in safety and also demonstrate your commitment to keeping them safe.
These regular inspections do not take the place of your normal incident reporting procedure and you should continue to report incidents as normal.
Implement a preventative maintenance schedule
It is vital that all of your plant and equipment is safe and in good working order. Make sure that you record all of your plant and equipment (including hand tools) in a register. This register should form the basis of your regular preventative maintenance schedule. Make sure you check the schedule regularly to ensure that any faulty plant or equipment is in good working order.
You can get good information on the maintenance required by referring to manufacturer manuals or websites.
Design and implement a simple incident and accident reporting procedure
Put in place reporting procedures that make it easy for your workers to let you know whenever an incident occurs; and encourage them to do so. Make sure you train all of your workers and managers in these procedures.
Make sure that you investigate each incident that occurs and that you record the outcomes. Involve your workers in the investigations and let them know what the results of any investigations are. Ensure that all required corrective actions are recorded and that there is a clear accountability for closing out any actions. Follow up corrective actions to make sure they are done.
Implement an emergency plan for all types of emergencies – not just fire
Most organisations have a fire emergency and evacuation plan but there are other kinds of emergencies that can arise. Make sure you have plans in place for medical emergencies, bomb threats, chemical spills or other major events.
Consider:
- the impact an emergency would have on the workplace and any nearby workplaces
- how workers and visitors would safely exit the workplace
- where to locate a safe emergency assembly point
- how you would make sure that everyone has safely exited the workplace
- what specific training is needed (e.g. fire warden, first aid, fire extinguishers etc.).
Once the plan is developed you will need to provide training and instruction to all of your workers to make sure they know what to do in the event of an emergency.
Useful links
You are unlikely to have any processes in place for ensuring that your workplace is safe.
This score indicates that you need to take immediate action to ensure you maintain a safe workplace.
What you can do to improve:
Design and implement a process to carry out regular safety checks
You need to set up a system of regular safety inspections of your worksite. These inspections should be scheduled and there should be checks performed to make sure they occur as planned. Once you have established a routine, it is a good idea to have a regular rotation of people doing the inspection including managers, supervisors and workers.
Any issues you note as part of these inspections should be documented and actioned. Always inform workers that this has occurred as it will help keep them involved in safety and also demonstrate your commitment to keeping them safe.
These regular inspections do not take the place of your normal incident reporting procedure and you should continue to report incidents as normal.
Implement a preventative maintenance schedule
It is vital that all of your plant and equipment is safe and in good working order. Make sure that you record all of your plant and equipment (including hand tools) in a register. This register should form the basis of your regular preventative maintenance schedule. Make sure you check the schedule regularly to ensure that any faulty plant or equipment is in good working order.
You can get good information on the maintenance required by referring to manufacturer manuals or websites.
Design and implement a simple incident and accident reporting procedure
Put in place reporting procedures that make it easy for your workers to let you know whenever an incident occurs; and encourage them to do so. Make sure you train all of your workers and managers in these procedures.
Make sure that you investigate each incident that occurs and that you record the outcomes. Involve your workers in the investigations and let them know what the results of any investigations are. Ensure that all required corrective actions are recorded and that there is a clear accountability for closing out any actions. Follow up corrective actions to make sure they are done.
Implement an emergency plan for all types of emergencies – not just fire
Most organisations have a fire emergency and evacuation plan but there are other kinds of emergencies that can arise. Make sure you have plans in place for medical emergencies, bomb threats, chemical spills or other major events.
Consider:
- the impact an emergency would have on the workplace and any nearby workplaces
- how workers and visitors would safely exit the workplace
- where to locate a safe emergency assembly point
- how you would make sure that everyone has safely exited the workplace
- what specific training is needed (e.g. fire warden, first aid, fire extinguishers etc.).
Once the plan is developed you will need to provide training and instruction to all of your workers to make sure they know what to do in the event of an emergency.
Useful links
You are unlikely to have a system that documents safety incidents and lets you identify safety issues and develop prevention strategies.
Your responses indicate that you need to take immediate action to ensure that you have a documented system to report and investigate safety incidents and injuries. Your procedure must also include management review and reporting.
What you can do to improve:
Develop and implement a simple and effective incident reporting procedure
Involve your workers in developing a simple to use and effective incident reporting procedure. Your goal is to make it easy for your workers to report incidents and injuries and easy for you to investigate them.
When developing your procedure consider:
- What incidents, hazards or injuries are to be reported (e.g. unsafe equipment, chemical spills, injuries, near-misses etc.)?
- To whom will the incidents be reported? Make sure the nominated person is someone who has the authority to act upon the report such as a manger or senior person.
- How will incidents be reported? Make sure the procedure addresses how a worker will report issues and requires management to act upon the report and provide feedback to the reporting worker.
- Who will investigate the incident? It would be a good idea to nominate a person (perhaps a safety officer or manager with appropriate training) to coordinate investigations and to be ultimately responsible for them. Ideally the investigation should involve all relevant people including the reporting worker, their manager/supervisor and the nominated investigator.
- How will corrective actions be recorded and closed out? Minor incidents will usually involve simple and immediate fixes (although these should still be recorded) but more serious incidents will require more complex actions. It is important that these are recorded and responsibility for closing them out assigned.
- How will incidents, injuries and investigations be reported to senior management? Consider how often incidents will be reported and reviewed by senior management and what the mechanism is for the reports (e.g. a weekly or monthly meeting with managers/supervisors, a written report etc.).
As part of the process you need to create a register of all incidents, investigations and outcomes. This is generally a simple summary of incidents that can be accessed easily. Examples of incident registers can be found on the SafeWork SA website.
Use your incident reports and register to help you improve your workplace safety
Incident reports and their associated investigations are a good source of information on the health of your work health and safety systems and general workplace safety.
Whenever you are reviewing your safety systems or your workplace always consider incident reports as they can help you identify adverse trends and help drive improved safety.
Useful links
You are unlikely to have a system that documents safety incidents and lets you identify safety issues and develop prevention strategies.
Your responses indicate that you need to take immediate action to ensure that you have a documented system to report and investigate safety incidents and injuries. Your procedure must also include management review and reporting.
What you can do to improve:
Develop and implement a simple and effective incident reporting procedure
Involve your workers in developing a simple to use and effective incident reporting procedure. Your goal is to make it easy for your workers to report incidents and injuries and easy for you to investigate them.
When developing your procedure consider:
- What incidents, hazards or injuries are to be reported (e.g. unsafe equipment, chemical spills, injuries, near-misses etc.)?
- To whom will the incidents be reported? Make sure the nominated person is someone who has the authority to act upon the report such as a manger or senior person.
- How will incidents be reported? Make sure the procedure addresses how a worker will report issues and requires management to act upon the report and provide feedback to the reporting worker.
- Who will investigate the incident? It would be a good idea to nominate a person (perhaps a safety officer or manager with appropriate training) to coordinate investigations and to be ultimately responsible for them. Ideally the investigation should involve all relevant people including the reporting worker, their manager/supervisor and the nominated investigator.
- How will corrective actions be recorded and closed out? Minor incidents will usually involve simple and immediate fixes (although these should still be recorded) but more serious incidents will require more complex actions. It is important that these are recorded and responsibility for closing them out assigned.
- How will incidents, injuries and investigations be reported to senior management? Consider how often incidents will be reported and reviewed by senior management and what the mechanism is for the reports (e.g. a weekly or monthly meeting with managers/supervisors, a written report etc.).
As part of the process you need to create a register of all incidents, investigations and outcomes. This is generally a simple summary of incidents that can be accessed easily. Examples of incident registers can be found on the SafeWork SA website.
Use your incident reports and register to help you improve your workplace safety
Incident reports and their associated investigations are a good source of information on the health of your work health and safety systems and general workplace safety.
Whenever you are reviewing your safety systems or your workplace always consider incident reports as they can help you identify adverse trends and help drive improved safety.
Useful links
Need more help?
SafeWork SA
SafeWork SA’s WHS advisors can visit your workplace to help you understand your work health and safety responsibilities as well as provide practical support to improve your systems, practices and general approach to safety.
Phone: 1300 365 255
help.safework@sa.gov.au
www.safework.sa.gov.au
Twitter: @SafeWorkSA
Facebook: @safeworksa
ReturnToWorkSA
Phone: 13 18 55
Injury prevention: injuryprevention@rtwsa.com
Mentally healthy workplaces: mentallyhealthy@rtwsa.com
Return to work coordinator support service: coordinators@rtwsa.com
Action plan
| Hazard/Risk | Actions | Responsible | Review Date | Due Date | Complete Date | Comments |
|---|








 Date printed: 25 Feb 2026
Date printed: 25 Feb 2026